In other words, it’s your money, not the bank’s, so it’s not considered a bank asset. Contributions represent the amount of money invested in a company by its owners, while taxes represent the amount of money owed to the government. These are amounts owed by a company that will not be due for at least one year from the date of the balance sheet. Accounts receivable are amounts owed to a company by its customers for goods or services that have been delivered but not yet paid for. Going back to our loan amortization schedule (Figure 3), the outstanding amount on the loan is $28,460 at the end of two years. We can see that there is a large difference of $18,460 between the value of the loan and the value of the asset.
Start a small business
- Current liabilities can include accounts payable, short-term debt, and accrued expenses, while non-current liabilities can include long-term loans, bonds, and deferred taxes.
- These obligations are typically paid off using current assets like cash or receivables.
- The latter is based on the current price of a stock, while paid-in capital is the sum of the equity that has been purchased at any price.
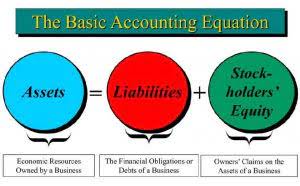
- The equity capital/stockholders’ equity can also be viewed as a company’s net assets.
- Suppose Company B has $5 million in assets but $4.5 million in liabilities.
- Please refer to the Payment & Financial Aid page for further information.
- They help investors, creditors, and other stakeholders understand how valuable the company is and whether it has enough resources to pay off all its debts if needed.
Liquidity and solvency ratios show how well a company can pay off its debts and obligations with existing assets. Long-term liabilities are debts and other non-debt financial obligations, which are due after a period of at least one year from the date of the balance sheet. For instance, a company may issue bonds that mature in several years’ time. Current liabilities are the company’s liabilities that will come due, or must be paid, within one year.
Definition of current assets
- A balance sheet shows a company’s financial position at a specific point in time.
- It happens when the value of the asset remains constant, but the amount of the loan balance goes up.
- On the basis of such evaluation, they anticipate the future performance of the company in terms of profitability and cash flows and make important economic decisions.
- If something changes and an investment no longer fits your objectives and risk tolerance, it might be time to move on.
- The second is the retained earnings, which includes net earnings that have not been distributed to shareholders over the years.
- Unlike shareholder equity, private equity is not accessible to the average individual.
If used in conjunction with other tools and metrics, the investor can accurately analyze the health of an organization. The balance sheet is interconnected with the profit and loss (P&L) statement and the cash flow statement, providing a full picture of a company’s what is total equity on a balance sheet financial health. The Current Ratio measures a company’s ability to pay off its short-term liabilities with its short-term assets. A higher ratio indicates that the company is better able to cover its short-term obligations. A ratio above 1 is generally considered healthy, as it means the company has more current assets than current liabilities. Net Current Assets represent the difference between a company’s current assets and current liabilities.
- Some call this value “brand equity,” which measures the value of a brand relative to a generic or store-brand version of a product.
- Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due for repayment over periods longer than one year.
- Aside from stock (common, preferred, and Treasury) components, the SE statement includes retained earnings, unrealized gains and losses, and contributed (additional paid-up) capital.
- It is important that all investors know how to use, analyze, and read a balance sheet.
Shareholders’ Equity

Recessions can sharply reduce asset values, particularly in sectors like real estate and manufacturing. Companies holding significant inventory or property may see their asset base shrink while liabilities remain unchanged. The 2008 financial crisis is a clear example, as many firms experienced steep declines in asset values. We accept payments via credit card, wire transfer, Western Union, and (when available) bank loan. Some candidates may qualify for scholarships or financial aid, which will be credited against the Program Fee once eligibility is determined.
Amortisation only applies to intangible assets with a definite life (e.g., a 5-year software licence). Intangible assets with an indefinite life, like goodwill, are not amortised but are Online Accounting tested annually for impairment. Below, we’ll explain how each of these methods works, starting with depreciation and amortisation for tangible and intangible assets, followed by impairment, which applies to both. This account includes the amortized amount of any bonds the company has issued. It can be sold at a later date to raise cash or reserved to repel a hostile takeover. Some liabilities are considered off the balance sheet, meaning they do not appear on the balance sheet.
Analysts use various financial ratios derived from balance sheet data to evaluate the health of a business, such as the current ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, and return on equity. If your business has strong fundamentals and isn’t financing all of its growth with debt, your owner’s equity should be increasing with time. Understanding equity and being able to track its growth real estate cash flow is crucial to understanding the long-term financial health of a business. Shareholder equity is the difference between a firm’s total assets and total liabilities.

What does the balance sheet formula represent?
Non-current liabilities are obligations that are not expected to be settled within one year. Examples of non-current liabilities include long-term debt, leases, and bonds payable. To illustrate how a balance sheet is structured and functions, let’s examine a simplified example of a company’s balance sheet.